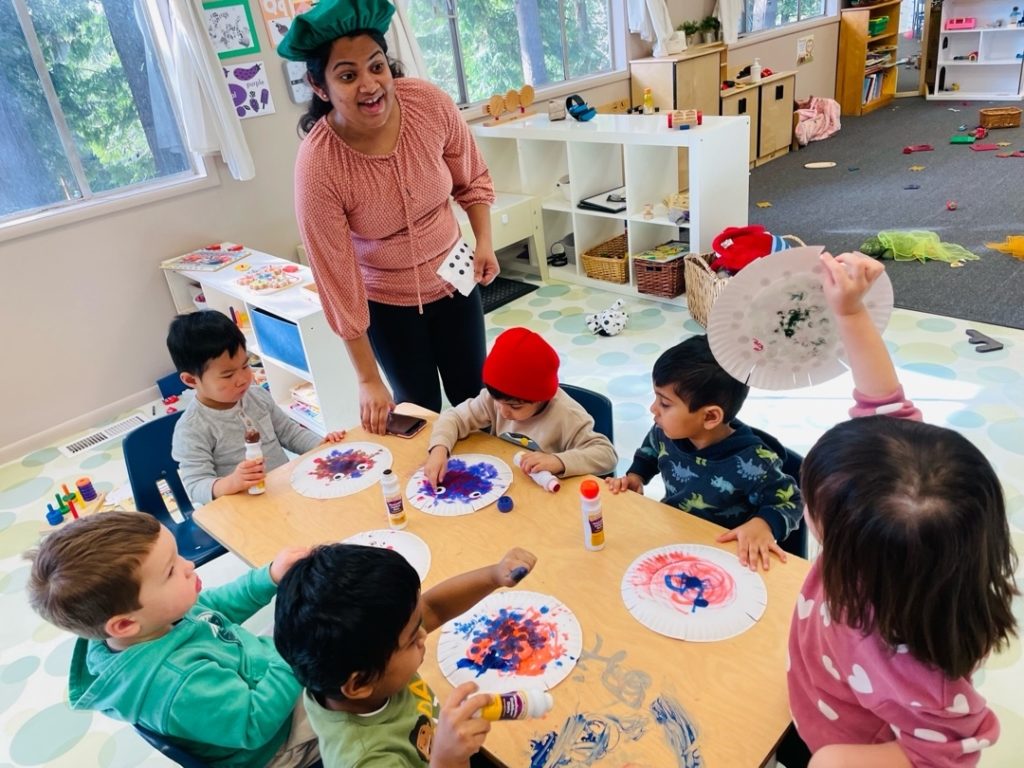
Being a toddler teacher, I have helped potty train many kids. It’s rarely easy, and it can be a very stressful experience for those who are not ready for it. Thankfully, there are tips, tricks, and plenty of resources out there to help along the way.
The Science of Potty Training
According to the Seattle Children’s Hospital, an infant does not have the muscle strength to control their bladder until around 18 months old. Just like with any skill, it is something that they will need patience in order to fully master.
The process is also different for girls and boys. The main reason for this is that it takes longer for boys to develop the muscle strength needed to control their bladder. Studies also suggest that girls simply become interested in using the potty earlier than boys do.
How to Know They’re Ready
Without knowing the signs, it can be hard to find the right time to potty train your child. A few things to look for:
- They start communicating, especially when they need a diaper change. Though this is often verbal, it may not always be; they can also make a face or tug at their pants/diaper.
- They start hiding or seeking privacy when they go.
- They start
s having more “scheduled” bowel movements.
- Their diaper stays dry for longer periods of time.
- Generally, they show a desire for more independence.
Don’t Start Too Early
Rushing a toddler into underwear before they’re ready is a common mistake. This can be a point of much frustration (both to the caregiver and the child), as well as cause an unhealthy relationship with the potty.
It may also cause health concerns. It may cause them to be a “chronic holder” who holds their bladder longer than is healthy (Cleveland Clinic). This can lead to urinary tract infections or constipation.
Accept that Accidents Happen.
While accidents can be frustrating and unpleasant to clean up, it’s all a part of the process. When this happens, it’s important to stay calm and reassure them. Then ask the children to change themselves and help me clean up the mess.
When you get mad about an accident, it can often lead to them being scared, which can then cause more accidents.
Choosing the Best Method.
There are many ways to potty train your child. Not every method will work for you or your child, so use what is best for your family.
If your child is in school, be sure to communicate your plan with your child’s teacher so that they can help and keep consistency.
3-Day Method: How to Potty Train Your Child in 3 Days: Potty Training Tips (verywellfamily.com)
This method is very hands-on and requires you to stay with your child for 3 days. While effective, it requires you to put everything aside and focus only on potty training for the full 3 days, which is not always viable.
Child-Oriented Method: Child-Oriented Potty Training – BabySparks
This is what I personally use in my classroom. As the name suggests, it focuses more on the child’s desire to begin potty training and does not have a “deadline.”
Parent-Lead Method: The Only Potty Training Schedule You’ll Ever Need | WonderBaby.org
Also known as the “Schedule Method,” this one is used for parents who like to follow a strict schedule. It can be combined with either the 3-Day or the Child-Oriented method.
Changing Circumstances
As with any developmental skill, potty training can be affected by major events in a child’s life. It’s very common for a child who has already been potty trained to suddenly start having accidents again if something changes at home, such as the birth of a new baby, a family move, a new school, or even a vacation. It is also not uncommon for a child to have accidents when they get sick.
If it lasts longer than a week and is turning into a pattern, then the child may be experiencing regression. Regression is different than the odd accident out of the blue, or even a short string of accidents that happen within a few days.
What to Do When Regression Happens
Regression does not happen only with potty training. It can also be seen in social skills, language, emotional regulation, or just about any domain (Cleveland Clinic). It’s also not uncommon to see it happen at any age, even well into elementary school.
If a regression does happen, it’s important to assure your child that you are there to support them. Do not put any undue pressure on them, but make sure that the potty is accessible.
You can also try to determine the reason for regression. Was there a change at home, or is it something medical going on? Once you know what is causing the accidents, you can look for a way to help.
The Cleveland Clinic explains many ways to help with regression: Potty-Training Regression: What To Do – Cleveland Clinic
What About Bed-Wetting?
Bed-wetting is very normal (especially in boys) and can persist for many years after a child has been fully potty trained. It can be caused by many things – health concerns, psychological reasons, or even lack of control while sleeping.
In most cases, it goes away by age 6 (Cleveland clinic). If it is happening consistently (at least 2 times a month) after that point, don’t panic! It is always best to talk to your child’s pediatrician about any concerns you have.
Book of the Month: “Potty” by Leslie Patricelli.
A new toddler title charts a crucial achievement. There comes a point in a toddler’s life when going in one’s diaper is only one possible option, and the question must be raised: “Should I go in my potty?”
With pitch-perfect humor and pacing, Leslie Patricelli follows the inner dialogue (sure to have little ones shouting responses) and hilarious actions of everyone’s favorite Baby, winding up with an over-the-top look of surprise and delight that will have both parents and offspring laughing out loud–“I did it!”
Potty (Leslie Patricelli board books): Patricelli, Leslie, Patricelli, Leslie: 9780763644765: Amazon.com: Books
Sources:
Glowacki, J. (2015) Oh crap! potty training: Everything Modern Parents Need to Know to Do It Once and Do It Right. Gallery Books.
(2021) The best potty training tips, Cleveland Clinic. Cleveland Clinic. Available at: https://health.clevelandclinic.org/the-best-potty-training-tips/#:~:text=To%20help%20you%20reach%20toilet%20training%20nirvana%2C%20invest,clean-up%21%204%20Children%E2%80%99s%20books%20to%20pass%20the%20time. (Accessed: February 24, 2023).
Lonzer, D. (2022) Potty-Training Regression: What To Do About It, Cleveland Clinic. Cleveland Clinic. Available at: https://health.clevelandclinic.org/what-to-do-when-your-potty-trained-child-suddenly-isnt/ (Accessed: February 24, 2023).
Potty training your child – Seattle Children’s (no date) Seattle Children’s Hospital. Available at: https://www.seattlechildrens.org/health-safety/keeping-kids-healthy/development/toliet-potty-training/ (Accessed: February 24, 2023).